- Published on
设计模式(16)——迭代器 Iterator
- Authors

- Name
- Leon
十六、Iterator(迭代器模式,别名 Cursor 游标)
1. 意图:
提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示。
2. 适用:
- 访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示
- 支持对聚合对象的多种遍历
- 为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口(即,支持多态迭代)
3. 类图:
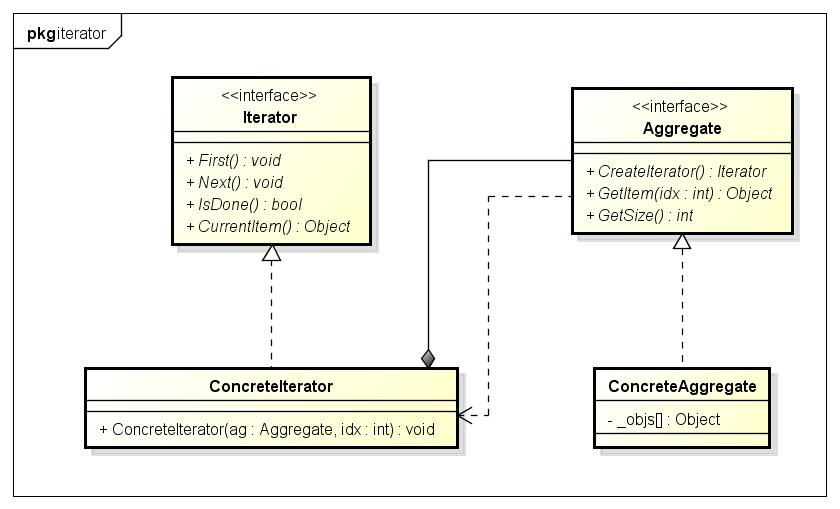
4. 例:
STL 模板库的中常见的容器类有List,Set,Map等,使用容器类经常需要遍历里面的所有元素,当对容器类中元素的组织方式不清楚时,要遍历元素不是一件容易的事情。迭代器就是解决这个问题的救星,它提供了一套统一的接口,如 begin(), next(), end(),所有的遍历都可以用这套接口来实现。这套接口具体由每个容器类来实现,容器内部才是最清楚怎么遍历自己元素的地方。正向遍历,反向遍历,中序遍历的需求可以通过由容器内部创建不同的 Iterator 来实现,而 Iterator 暴露的接口是一样的。
5. 中间层思考:
通过引入 Iterator 迭代器这个中间层,系统可以不需要直接操作容器的所有细节,只需要知道 Iterator 的标准接口就能操作容器的所有元素。Iterator 将系统和容器的细节解耦了,程序猿的生活也变得更加美好了。
6. C++实现:
- 编写聚合类接口
Aggreagte,聚合类ConcreteAggregate - 编写迭代器接口
Iterator,迭代器类ConcreteIterator,含有方法First()、Next()、CurrentItem()、IsDone() - 编写迭代器构造函数
ConcreteIterator(Aggregate* ag, int idx = 0),强关联一个聚合类对象。
Iterator.h
//Iterator.h
#pragma once
typedef int Object;
class Aggregate;
class Iterator {
public:
virtual ~Iterator();
virtual void First() = 0;
virtual void Next() = 0;
virtual bool IsDone() = 0;
virtual Object CurrentItem() = 0;
protected:
Iterator();
private:
};
class ConcreteIterator : public Iterator {
public:
ConcreteIterator(Aggregate* ag, int idx = 0);
~ConcreteIterator();
void First();
void Next();
bool IsDone();
Object CurrentItem();
protected:
private:
Aggregate* _ag;
int _idx;
};
Iterator.cpp
//Iterator.cpp
#include "Iterator.h"
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace::std;
Iterator::Iterator() {}
Iterator::~Iterator() {}
ConcreteIterator::ConcreteIterator(Aggregate* ag, int idx) {
this->_ag = ag;
this->_idx = idx;
}
ConcreteIterator::~ConcreteIterator() {}
Object ConcreteIterator::CurrentItem() {
return _ag->GetItem(_idx);
}
// 初始化迭代器
void ConcreteIterator::First() {
_idx = 0;
}
void ConcreteIterator::Next() {
if (_idx < _ag->GetSize())
_idx++;
}
bool ConcreteIterator::IsDone() {
return (_idx == _ag->GetSize());
}
Agrregate.h
//Aggregate.h
#pragma once
class Iterator;
typedef int Object;
class Aggregate {
public:
virtual ~Aggregate();
virtual Iterator* CreateIterator() = 0;
virtual Object GetItem(int idx) = 0;
virtual int GetSize() = 0;
protected:
Aggregate();
private:
};
class ConcreteAggregate : public Aggregate {
public:
enum{SIZE = 3};
ConcreteAggregate();
~ConcreteAggregate();
Iterator* CreateIterator();
Object GetItem(int idx);
int GetSize();
protected:
private:
Object _objs[SIZE];
};
Aggregate.cpp
//Agreggate.cpp
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include "Iterator.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace::std;
Aggregate::Aggregate() {}
Aggregate::~Aggregate(){}
ConcreteAggregate::ConcreteAggregate() {
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
_objs[i] = i;
}
}
ConcreteAggregate::~ConcreteAggregate() {}
Iterator* ConcreteAggregate::CreateIterator(){
return new ConcreteIterator(this);
}
Object ConcreteAggregate::GetItem(int idx) {
if (idx < this->GetSize()) {
return _objs[idx];
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int ConcreteAggregate::GetSize() {
return SIZE;
}
main.cpp
//main.cpp
#pragma once
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include "Iterator.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace::std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
Aggregate* ag = new ConcreteAggregate();
Iterator* it = new ConcreteIterator(ag);
for (; !(it->IsDone()); it->Next()) {
cout << it->CurrentItem() << endl;
}
return 0;
}